Data localization is the practice of storing and processing data within specific geographic boundaries. This requirement is often imposed by governments or regulatory bodies to ensure data privacy, security, and compliance with local laws.
For businesses operating in a globalized world, understanding and complying with data localization laws is crucial. Failure to do so can result in significant legal and financial penalties.
In today’s digital age, organizations amass vast amounts of data. Effective storage, management, and protection of this data are paramount. Data localization provides a framework for countries to regulate how data, particularly personal information, is handled. This ensures data protection, privacy, and compliance with local laws.
What is Data localization?
Data localization is the practice of storing and processing data within specific geographic boundaries. This requirement is often imposed by governments or regulatory bodies to ensure data privacy, security, and compliance with local laws.
In essence, data localization mandates that data collected from residents of a particular country or region must be stored and processed within that jurisdiction. This can help protect the privacy of individuals and prevent data from being transferred to countries with less stringent data protection laws.
Why Data Localization is Important for Businesses?

Data localization is a crucial consideration for businesses operating in today’s globalized world. It offers several significant benefits, including:
Enhanced data security and privacy: Storing data locally reduces the risk of data breaches and unauthorized access. When data is stored within a specific jurisdiction, it is less likely to be intercepted or compromised during cross-border transfers. This is particularly important for sensitive data such as personal information, financial data, and intellectual property.
Also Read – Multi-Cloud Strategy: Your Key to Simplifying the Complex
Improved customer trust: Demonstrating compliance with data localization laws can build trust with customers and clients. In today’s data-driven world, consumers are increasingly concerned about their privacy and the security of their personal information. By localizing data, businesses can demonstrate their commitment to data protection and privacy, which can lead to increased customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Reduced legal risks and penalties: Adhering to data localization regulations can help mitigate legal risks and avoid costly fines. Non-compliance with data localization laws can result in significant financial penalties, reputational damage, and even business disruption.
Enhanced operational efficiency: Localizing data can improve application performance and reduce latency. When data is stored closer to where it is accessed, applications can load faster and perform more efficiently. This can lead to improved user experience and increased productivity.
Compliance with industry-specific regulations: Certain industries, such as healthcare and finance, have specific data localization requirements that must be met to protect sensitive information and comply with regulatory standards. For example, the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) requires healthcare providers to maintain the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of protected health information (PHI). Failure to comply with HIPAA can result in severe penalties.
Understanding Data Localization Laws and Regulations
Several key data localization regulations have been implemented worldwide. Some of the most prominent include:
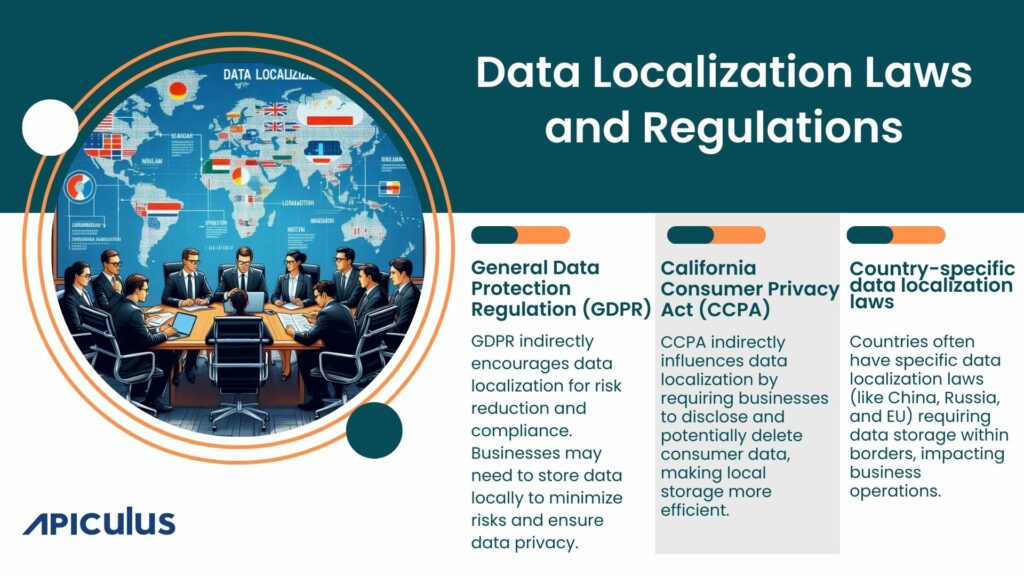
- General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR):
- While GDPR doesn’t explicitly require data localization, its principles of data minimization and accountability can indirectly impact data residency.
- Businesses may need to localize data to reduce the risk of data breaches and ensure compliance with the principle of data minimization, which requires storing only the necessary data.
- GDPR also includes provisions for data portability, which can impact where data is stored and processed.
- California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA):
- The CCPA requires businesses operating in California to disclose personal information collected from residents and provide them with certain rights regarding their data.
- While the CCPA doesn’t explicitly mandate data localization, it can indirectly impact data residency decisions. For example, if a business is required to delete a consumer’s data upon request, it may be more efficient to store that data locally.
- Country-specific data localization laws:
- Many countries have their own data localization laws, often driven by national security, economic, or cultural concerns.
- Examples include China’s Cybersecurity Law, Russia’s Personal Data Law, and the European Union’s e-Privacy Directive.
- These laws may require specific types of data to be stored within the country, or may impose restrictions on the transfer of data outside the country.
Also Read – On-Prem, Private, or Public? Choosing the Right Cloud Deployment Models for Your Business Needs
It’s important to note that data localization requirements can change over time, and businesses must stay updated on the latest regulations to ensure compliance. Additionally, some countries may have sector-specific data localization requirements, such as those applicable to financial institutions or healthcare providers.
Non-compliance with data localization laws can lead to hefty fines, reputational damage, and potential loss of business. It is essential to stay updated on the latest regulations and ensure your business is compliant.
What are the Benefits of Data Localization?
Data localization, also known as data residency, is the practice of storing and processing data within specific geographic boundaries. While often driven by regulatory compliance, data localization offers several tangible benefits for businesses.
Enhanced Data Security and Privacy – One of the primary advantages of data localization is the enhanced security and privacy it provides. By storing data locally, businesses can reduce the risk of data breaches and unauthorized access. Cross-border data transfers can increase the vulnerability of data to interception, hacking, or misuse. Localizing data helps to minimize these risks and protect sensitive information.
Improved Customer Trust and Satisfaction – Demonstrating compliance with data localization laws can significantly enhance customer trust and satisfaction. In today’s data-driven world, consumers are increasingly concerned about their privacy and the security of their personal information. By localizing data, businesses can reassure customers that their data is being handled responsibly and in accordance with local regulations. This can lead to increased customer loyalty, positive word-of-mouth, and improved brand reputation.
Reduced Legal Risks and Penalties – Non-compliance with data localization laws can result in severe legal consequences, including hefty fines, reputational damage, and even business disruption. By adhering to data localization regulations, businesses can mitigate these risks and avoid costly penalties. Additionally, compliance with data residency laws can demonstrate a commitment to responsible business practices and ethical behavior.
Also Read – The Future of Sovereign Cloud: Emerging Technologies and Trends
Enhanced Operational Efficiency – Localizing data can improve application performance and reduce latency. When data is stored closer to where it is accessed, applications can load faster and perform more efficiently. This can lead to improved user experience, increased productivity, and reduced operational costs.
Compliance with Industry-Specific Regulations – Certain industries, such as healthcare and finance, have specific data residency requirements that must be met to protect sensitive information and comply with regulatory standards. For example, the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) requires healthcare providers to maintain the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of protected health information (PHI). By localizing data, businesses in these industries can ensure compliance with relevant regulations and avoid penalties.
Challenges of Data Localization

Implementing a data localization strategy can present several significant challenges:
Technical Challenges:
- Data replication and synchronization: Replicating data across multiple geographic locations requires robust data replication and synchronization technologies. Ensuring data consistency and integrity can be complex, especially for large datasets.
- Infrastructure requirements: Setting up and maintaining data centers in specific regions can be costly and resource-intensive. Businesses may need to invest in new infrastructure, including servers, storage, and networking equipment.
- Data sovereignty and jurisdiction: Understanding the legal and regulatory implications of storing data in different jurisdictions is essential. Businesses may need to navigate complex legal frameworks and ensure compliance with local laws.
Cost Implications:
- Additional infrastructure costs: Setting up and maintaining data centers in specific regions can be expensive. Businesses may need to invest in new hardware, software, and personnel.
- Increased operational costs: Managing data across multiple locations can increase operational overhead, including costs for data management, security, and compliance.
- Potential for vendor lock-in: Relying on cloud providers or other third-party services for data residency can create vendor lock-in, limiting flexibility and increasing costs.
Limitations on Data Accessibility and Analysis:
- Increased latency: Accessing data stored in remote locations can introduce latency, which can impact application performance and user experience.
- Data silos: Localizing data can create data silos, making it difficult to access and analyze data from different locations. This can hinder data-driven decision-making and innovation.
- Data governance challenges: Ensuring data quality, consistency, and governance across multiple data centers can be complex and time-consuming.
Also Read – The Cloud Revolution: How Cloud as a Service (CaaS) is Reshaping IT
Balancing Data Localization with Global Business Operations:
- Maintaining data consistency: Ensuring data consistency across multiple locations can be challenging, especially when dealing with large datasets and complex data workflows.
- Supporting global collaboration: Data localization can make it more difficult for teams in different regions to collaborate and share data effectively.
- Adapting to changing business needs: Businesses may need to adjust their data localization strategy to accommodate changes in business operations, regulatory requirements, or market conditions.
Addressing these challenges requires careful planning, investment, and a comprehensive data localization strategy. Businesses should carefully evaluate the potential benefits and drawbacks of data localization before making a decision.
Implementing a Data Localization Strategy

Implementing a data localization strategy requires careful planning, execution, and ongoing monitoring. Here are the key steps involved:
- Assess your current data landscape: Identify where data is currently stored and processed. This includes understanding the location of data centers, cloud platforms, and any third-party services used to store and process data.
- Identify data localization requirements: Determine which regulations apply to your business and where data needs to be stored. This may involve researching specific data localication laws in the countries or regions where you operate.
- Develop a data localization roadmap: Create a detailed plan outlining the steps necessary to migrate data to the required locations. This roadmap should include timelines, resource allocation, and potential challenges.
- Choose the right data localization technologies and tools: Select appropriate tools for data replication, synchronization, and security. These tools may include data replication software, cloud platforms with data residency options, and encryption technologies.
- Implement data localization measures: Put your data residency plan into action. This may involve migrating data to new data centers, configuring cloud platforms for data residency, and implementing security measures to protect data in transit and at rest.
- Monitor and compliance: Continuously monitor your data localization efforts to ensure compliance with regulations and address any emerging challenges. This may involve conducting regular audits, reviewing data access logs, and staying updated on changes in data localization laws.
Additional Considerations:
- Data sovereignty: Understand the legal and regulatory implications of storing data in different jurisdictions. Consider factors such as data privacy laws, data protection authorities, and potential legal risks.
- Data quality and consistency: Ensure that data is consistent and accurate across different locations. This may involve implementing data governance practices and using data quality tools.
- Vendor lock-in: Be mindful of vendor lock-in when choosing data localization solutions. Consider using open-source technologies or cloud platforms that offer flexibility and avoid vendor dependency.
- Scalability: Your data localization strategy should be scalable to accommodate future growth and changes in business needs.
- Cost-effectiveness: Evaluate the costs associated with data localization, including infrastructure expenses, data transfer costs, and additional personnel requirements.
Also Read – Creating a Cloud Exit Strategy: A Guide to Cloud Repatriation
By following these steps and addressing the challenges involved, businesses can effectively implement a data localization strategy that ensures compliance with regulations, protects data privacy, and supports their global operations.
Apiculus: Your Data Localization Partner
Apiculus is a comprehensive cloud management platform designed to empower businesses in navigating the complexities of data localization. Our platform offers a suite of tools and features to ensure that your data is stored and processed in accordance with applicable regulations.
By choosing Apiculus, you gain access to a unified platform for managing your entire data landscape, simplifying data residency efforts. Our robust data governance features help you establish and maintain compliance with data residency laws. Apiculus also provides tools for seamless data migration and replication across different geographic locations, ensuring data consistency and security.
Free Download – In-Country Public Cloud Free e-Book Download
Our platform incorporates advanced security measures to protect your data from unauthorized access and breaches. Additionally, Apiculus can be easily integrated with your existing IT infrastructure, minimizing disruption and complexity.
With Apiculus, you can scale your data residency efforts to accommodate growth and changes in business needs. Our platform is designed to be flexible and adaptable, ensuring that you can meet evolving data localization requirements.
By choosing Apiculus, you can simplify data localication, reduce risks, enhance security, improve operational efficiency, and ensure compliance with relevant regulations. Contact us today to learn more about how our platform can benefit your business.
Conclusion
Data localization is a critical consideration for businesses operating in today’s globalized world. By understanding the relevant laws and regulations, implementing effective strategies, and leveraging tools like Apiculus, businesses can ensure compliance, protect their data, and maintain customer trust.
Apiculus offers comprehensive solutions to help businesses navigate the complexities of data localization. Our platform provides tools for data management, governance, and compliance, ensuring that your data is stored and processed in accordance with applicable regulations.
Also Read – Navigating Data Localization Laws: Key Considerations for Global Enterprises
Contact us today to learn more about how Apiculus can help your business achieve its data localization goals.

